Today, we’re diving into the world of Global Clinical Practice, or GCP. If you’re involved in clinical research or just a curious reader, understanding GCP is crucial. GCP is a set of internationally well-recognized ethical and scientific quality standards for designing, conducting, recording, and reporting trials involving human subjects. It’s all about ensuring clinical trials’ safety, integrity, and credibility. The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) plays a key role in establishing GCP. Ready to learn more?
Let’s get started!
The GCP Guidelines
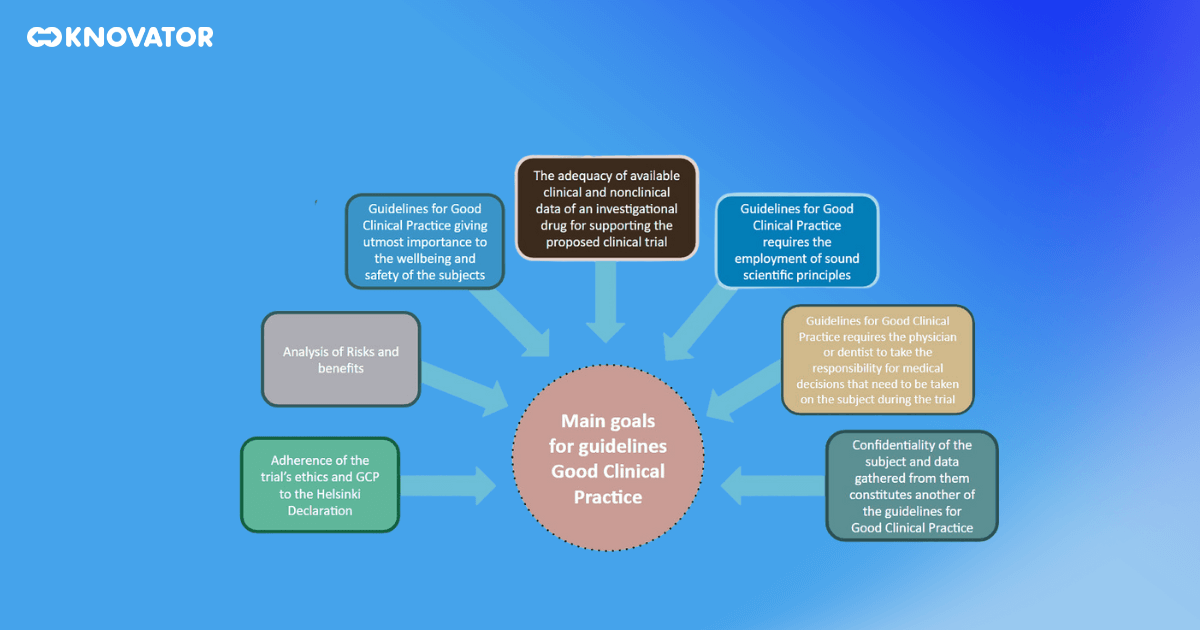 The GCP guidelines are the backbone of Global Clinical Practice. They are internationally recognized ethical and scientific quality standards that dictate how clinical trials involving human subjects should be designed, conducted, recorded, and reported. The guidelines cover every aspect of a clinical trial, from its inception to its conclusion.
The GCP guidelines are the backbone of Global Clinical Practice. They are internationally recognized ethical and scientific quality standards that dictate how clinical trials involving human subjects should be designed, conducted, recorded, and reported. The guidelines cover every aspect of a clinical trial, from its inception to its conclusion.
The guidelines point out the roles and responsibilities of all parties involved in a clinical trial. This includes institutional review boards (IRBs), which are responsible for reviewing and approving the trial protocol to protect the rights and welfare of the trial subjects. Clinical research investigators, who conduct the trial and collect the data, are guided in ensuring the trial is conducted ethically and scientifically. Clinical trial sponsors fund the trial and are responsible for ensuring the trial is properly managed and monitored. Monitors, who oversee the conduct of the trial, are guided on how to ensure the trial is conducted, recorded, and reported as per the protocol.
The GCP guidelines also provide detailed standards for conducting clinical trials. They cover the trial’s design, including the development of a clear, detailed protocol, the selection and withdrawal of subjects, the collection and reporting of data, and the analysis and interpretation of results. They also cover the handling of essential documents, the management of investigational products, and the procedures for dealing with adverse events.
But why are these guidelines so important? They ensure that trial subjects’ safety, rights, and well-being are protected and that the data generated from the trials are credible and accurate. In other words, they’re all about ensuring that clinical trials are conducted in a way that respects both the participants and the science.
History of GCP
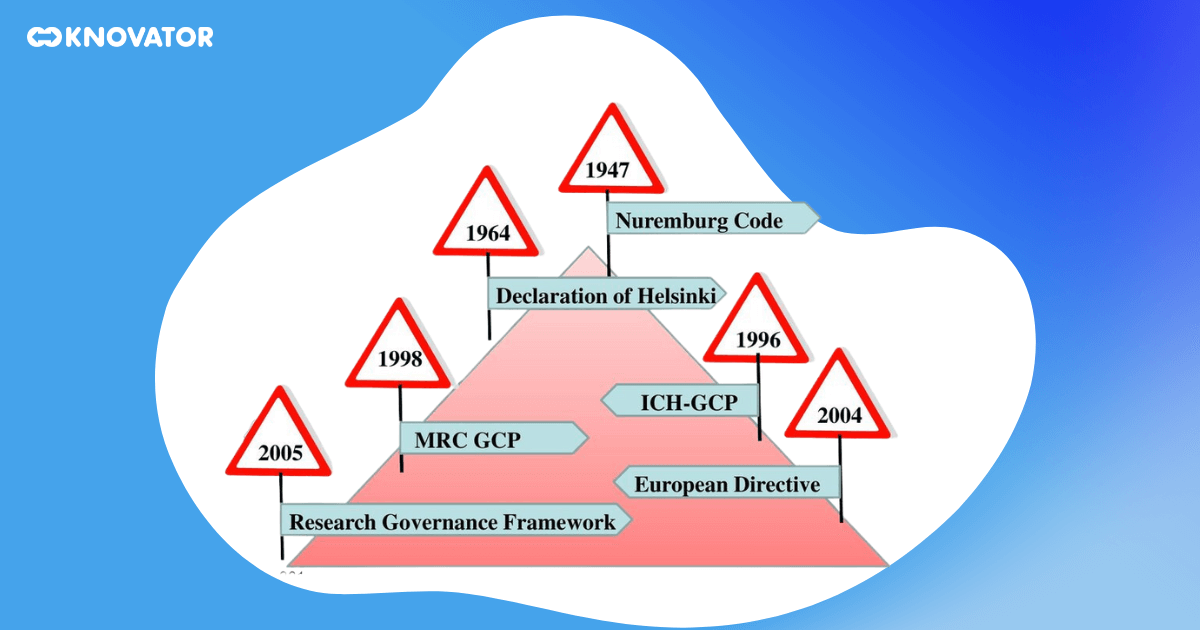 The history of GCP and ICH guidelines is a fascinating journey reflecting clinical research’s evolution over the past few decades. It all started in the US and Europe, with the need to establish common technical standards for pharmaceutical products. The goal was to ensure these products’ safety and efficacy and facilitate their approval and registration.
The history of GCP and ICH guidelines is a fascinating journey reflecting clinical research’s evolution over the past few decades. It all started in the US and Europe, with the need to establish common technical standards for pharmaceutical products. The goal was to ensure these products’ safety and efficacy and facilitate their approval and registration.
This led to the creation of the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) in 1990. The ICH is a unique global partnership between regulatory authorities and the pharmaceutical industry. Its mission is to promote public health by developing and promoting harmonized standards and guidelines for developing, registering, post-approval, and pharmacovigilance pharmaceutical products.
The ICH developed the GCP guidelines, which have since been adopted worldwide. These guidelines have revolutionized the conduct of clinical trials, setting the bar for quality, safety, and efficacy. They have also facilitated the global development and registration of pharmaceutical products, reducing duplication of testing and enabling the more efficient use of resources.
The development of the GCP guidelines was a significant milestone in the history of clinical research. It marked a shift from national to international standards, reflecting the increasingly global nature of clinical research. It also marked a shift from a focus on the product to a focus on the process, reflecting the increasing recognition of the importance of the conduct of clinical trials in ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
Impact of GCP
 The impact of GCP on clinical research is undeniable. It’s been endorsed globally, shaping how clinical trials are conducted and reported. By standardizing the conduct of trials, GCP has made trial findings more reliable and credible.
The impact of GCP on clinical research is undeniable. It’s been endorsed globally, shaping how clinical trials are conducted and reported. By standardizing the conduct of trials, GCP has made trial findings more reliable and credible.
But the influence of GCP goes beyond just trials. It’s also shaped the development of new drugs and treatments, pushing researchers and pharmaceutical companies to aim for the highest safety and efficacy standards. In doing so, GCP has contributed to the advancement of medical science and helped develop new treatments that have improved the health and well-being of people worldwide.
GCP has also had a significant impact on the protection of patient rights. By setting clear standards for the ethical conduct of clinical trials, GCP has helped to protect the safety, rights, and well-being of trial subjects. This has increased public trust in clinical research and has encouraged more people to participate in clinical trials.
The impact of GCP extends even further when we consider its role in regulatory decision-making. By providing a common set of standards for the conduct of clinical trials, GCP has facilitated the worldwide development and registration of pharmaceutical products. It has made it easier for regulatory authorities to review and approve new drugs, benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.
Legal and Regulatory Status of GCP
 GCP holds a significant legal and regulatory status in the European Union and the United States. In the EU, the Clinical Trial Regulation enforces adherence to GCP guidelines. This regulation sets out the rules for conducting clinical trials in the EU, including the requirements for protecting trial subjects, the quality and safety of investigational products, and the reliability and robustness of data.
GCP holds a significant legal and regulatory status in the European Union and the United States. In the EU, the Clinical Trial Regulation enforces adherence to GCP guidelines. This regulation sets out the rules for conducting clinical trials in the EU, including the requirements for protecting trial subjects, the quality and safety of investigational products, and the reliability and robustness of data.
Over in the US, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the implementation of GCP in clinical trials. The FDA has incorporated the GCP guidelines into its regulations, making adherence to GCP a legal requirement for clinical trials conducted in the US. The FDA also conducts inspections of clinical trial sites to ensure compliance with GCP and other regulations.
These regulatory bodies ensure that clinical trials comply with GCP guidelines in their jurisdictions. They conduct inspections, review trial data, and have the authority to take action against those who violate GCP standards. This regulatory oversight is crucial in maintaining the integrity of clinical trials and protecting the rights and safety of trial subjects.
Criticism of GCP
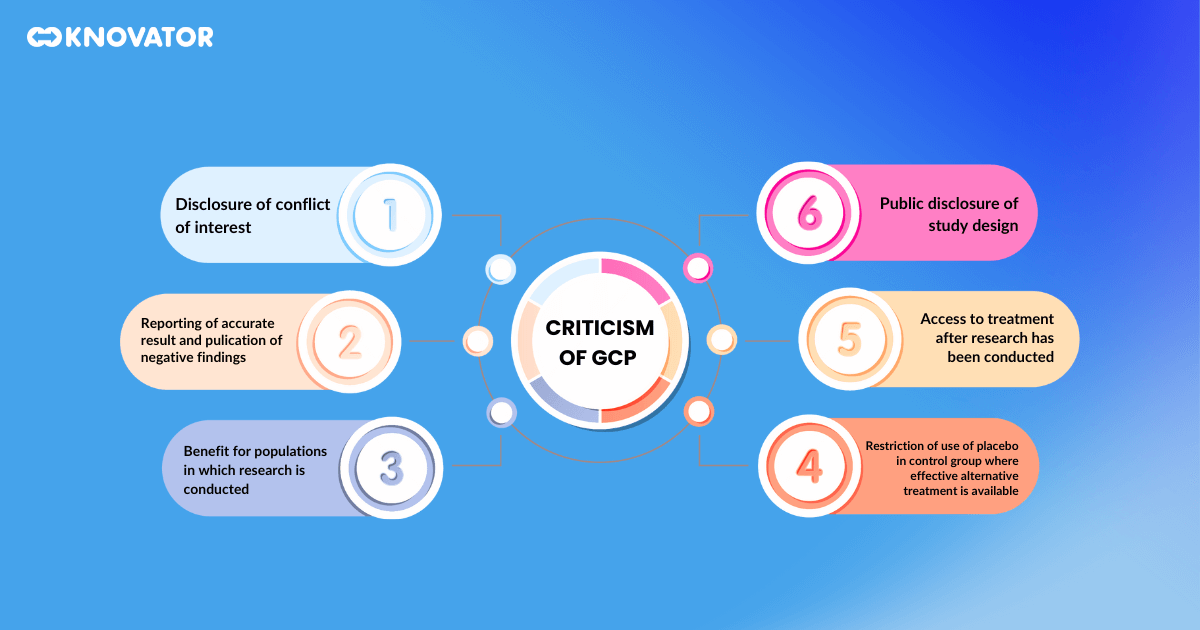 While GCP has made significant contributions to clinical research, it’s not without its critics. Some compare it with the Declaration of Helsinki, a set of ethical principles for medical research on human subjects developed by the World Medical Association. Critics argue that GCP lacks the moral principles and guidance found in the Declaration, such as the requirement for the benefits of research to outweigh the risks and the respect for the autonomy and dignity of research subjects.
While GCP has made significant contributions to clinical research, it’s not without its critics. Some compare it with the Declaration of Helsinki, a set of ethical principles for medical research on human subjects developed by the World Medical Association. Critics argue that GCP lacks the moral principles and guidance found in the Declaration, such as the requirement for the benefits of research to outweigh the risks and the respect for the autonomy and dignity of research subjects.
Critics also point out that GCP can be overly bureaucratic and rigid, potentially stifling innovation and slowing the development of new treatments. They argue for a more flexible approach that balances the need for rigorous standards with the need for innovation and efficiency.
Despite these criticisms, the importance of GCP in ensuring clinical trials’ safety, integrity, and credibility cannot be overstated. It remains a cornerstone of clinical research, setting the standards for conducting and reporting trials.










